

Radiculomedullopial arteries are those which happen to supply both anterior and posterior spinal systems simultaneously, sometimes via a coronary artery, and at other times via separate connections to the posterior spinal system. For a more complete discussion of spinal vasculature, see Spinal Vascular Anatomy section, particularly Spinal Arterial Anatomy.Ĭlassical dispostion depicts AICA and SCA arising from the basilar artery, in addition to multiple short basilar perforators whose supply is limited to the brainstem. Radiculopial arteries are those which supply the posterior spinal system. In practice, as you know, the radiculomedullary and radiculopial arteries are fewer, and may arise from longitudinal vessels other than the vert. The entire spinal cord system is supplied via segmental radiculomedullary arteries, which connect the vertebral artery to the anterior spinal artery. A number of perforating arteries into the substance of the cord exist when arising from the anterior spinal artery and penetrating through the ventral cord sulcus, they are named “sulco-comissural” arteries. The anterior and posterior spinal systems are connected by anastomoses running along the circumference of the cord, although known as “coronary” arteries, are conceptually quite clear. It has a variable territory depending on the size of the AICA ( AICA-PICA dominance).The image on the LEFT represents cervical spinal cord arterial supply, which consists of the anterior spinal artery and a paired, loose network of posterolateral vessels known as the posterior spinal arteries, and which are conceptually represented here as contiguous vessels (which is at least mostly true in the cervical spine). Note: occasionally, a small vertebral artery will terminate into a common AICA-PICA complex. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery gives off the following arteries: Supplies the vermis and adjacent hemisphere The main trunk of the posterior inferior cerebellar artery usually bifurcates somewhere along the margin of the cerebellar tonsil into Supplies branches to the cerebellar surface Marks the transition between the proximal (medulla-supplying) and distal (cerebellum-supplying) parts of the posterior inferior cerebellar arteryĬourses in the cleft between the tela choroidea, inferior medullary velum rostrally, and superior pole of the cerebellar tonsil caudallyĬontains the cranial loop, also known as the choroid point or choroid arch, an upward convex loop that has a constant relation to the 4 th ventricle and gives rise to choroidal arteries
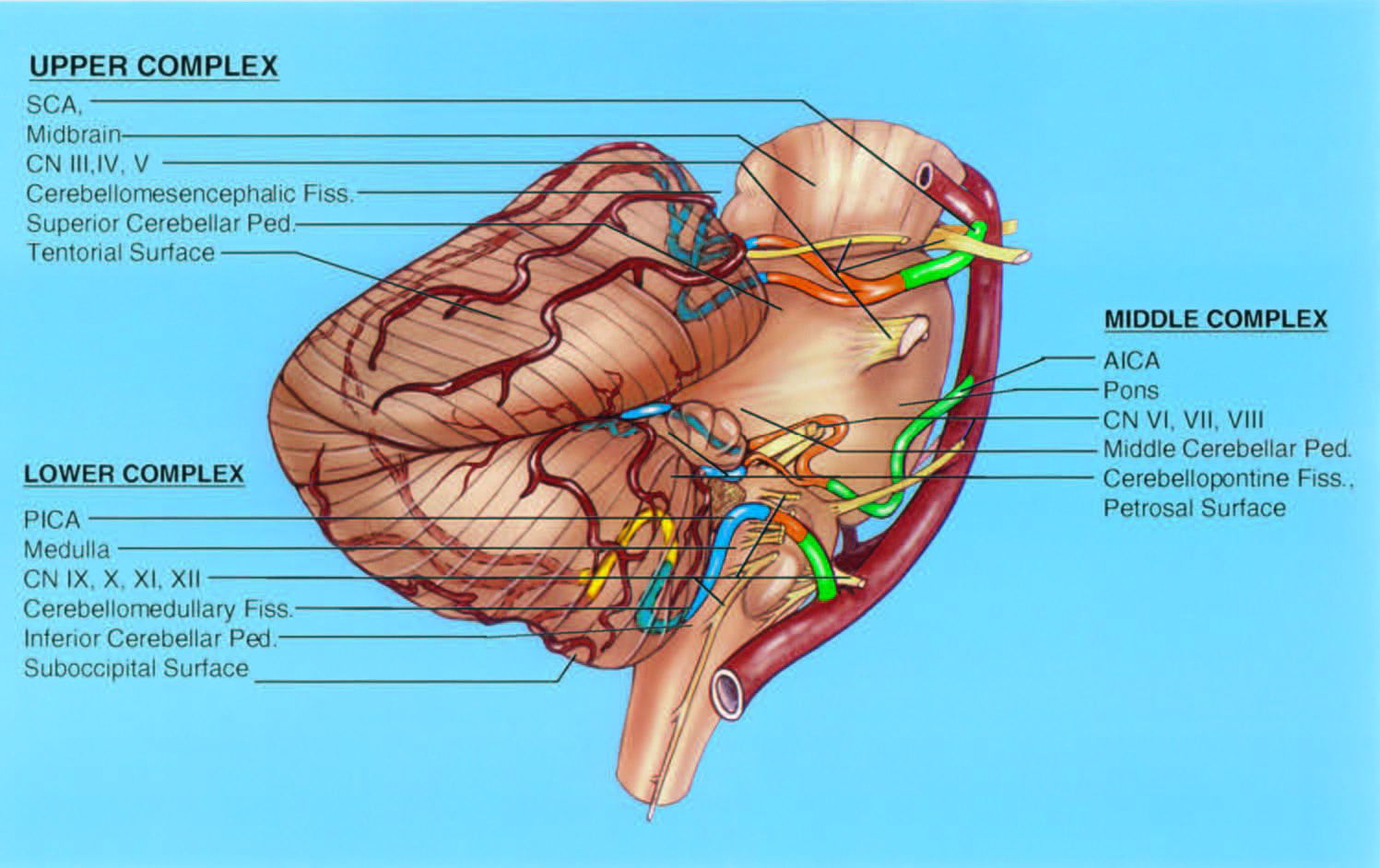
Variably courses (ascending or descending) along the side of the medulla near or between the origins of the 9 th, 10 th, and 11 th cranial nerve rootsĬourses along the posterolateral surface of the medulla and inferior cerebellar tonsilĬontains the caudal loop, a downward convex loop that mostly remain superior to the foramen magnum but occasionally extend below it 6,7:Ĭourses along the front of the medulla at the level of the inferior olive The segmental anatomy was defined microsurgically by Lister et al. Occasionally arises from a common origin with the anterior inferior cerebellar artery ~20% arise extracranially, inferior to the foramen magnumġ0% arise from the basilar rather than vertebral artery The PICA is a paired artery that originates from the vertebral artery V4 segment.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
